FAQs¶
- Q:
- How should I install MetAMOS?
- A:
- We recommend using the provided INSTALL.py script, that will retrieve and compile are requisite dependencies. As a shortcut we provide a PyInstaller-powered frozen binary; this is primarily for users who are experiencing extreme difficulties installing via INSTALL.py.
- Q:
- Where are my $#%^! results ?!?
- A:
- See here and here. If you still have questions, contact the dev team.
- Q:
- Why is the FindORFs step taking so long to complete?
- A:
- FragGeneScan is the default metagenomic gene caller; to improve performance we suggest acquiring a license to incorporate MetaGeneMark into your MetAMOS install.
- Q:
- What steps can I skip?
- A:
- Most of them! required steps are currently: Preprocess, Scaffold, and Postprocess.
- Q:
- Should I trim my input data?
- A:
iMetAMOS supports EA-UTILS as a trimming option, though it is disabled by default. We have found that some assemblers that build-in their own trimming module are hampered by pre-trimming the data. In contrast, assembler that do not have a trimming module can benefit from trimming input sequences. To enable trimming using EA-UTILS, a trimming option can be specified to runPipeline
$ -t eautils
- We compared assembler performance on trimmed and untrimmed data for the GAGE-B MiSeq Rhodobacter sphaeroides dataset. Overall, the largest corrected N50 was generated using the untrimmed data. The figure below shows assembler performance on untrimmed data
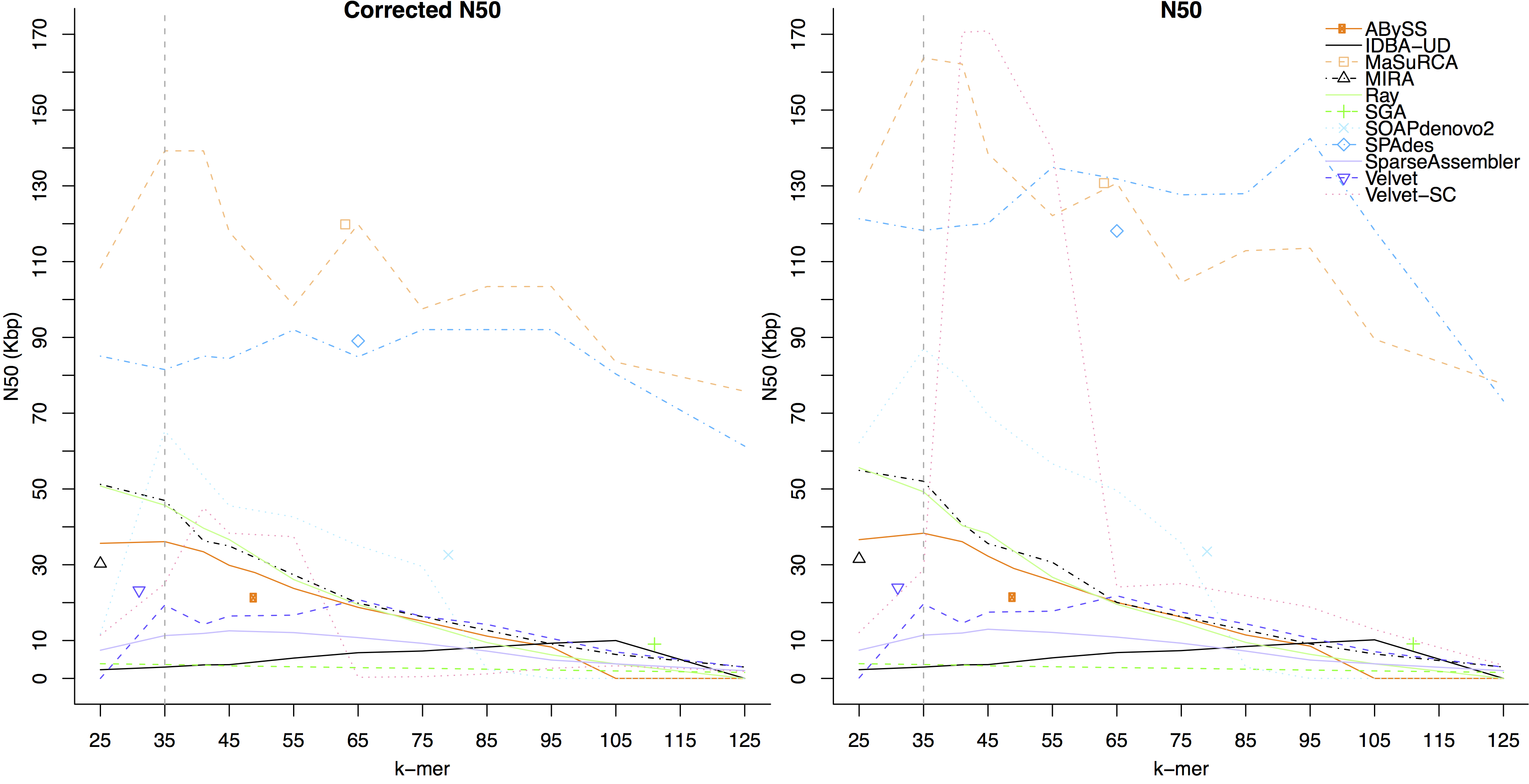
- The figure below shows assembler performance on the same dataset after trimming by EA-UTILS
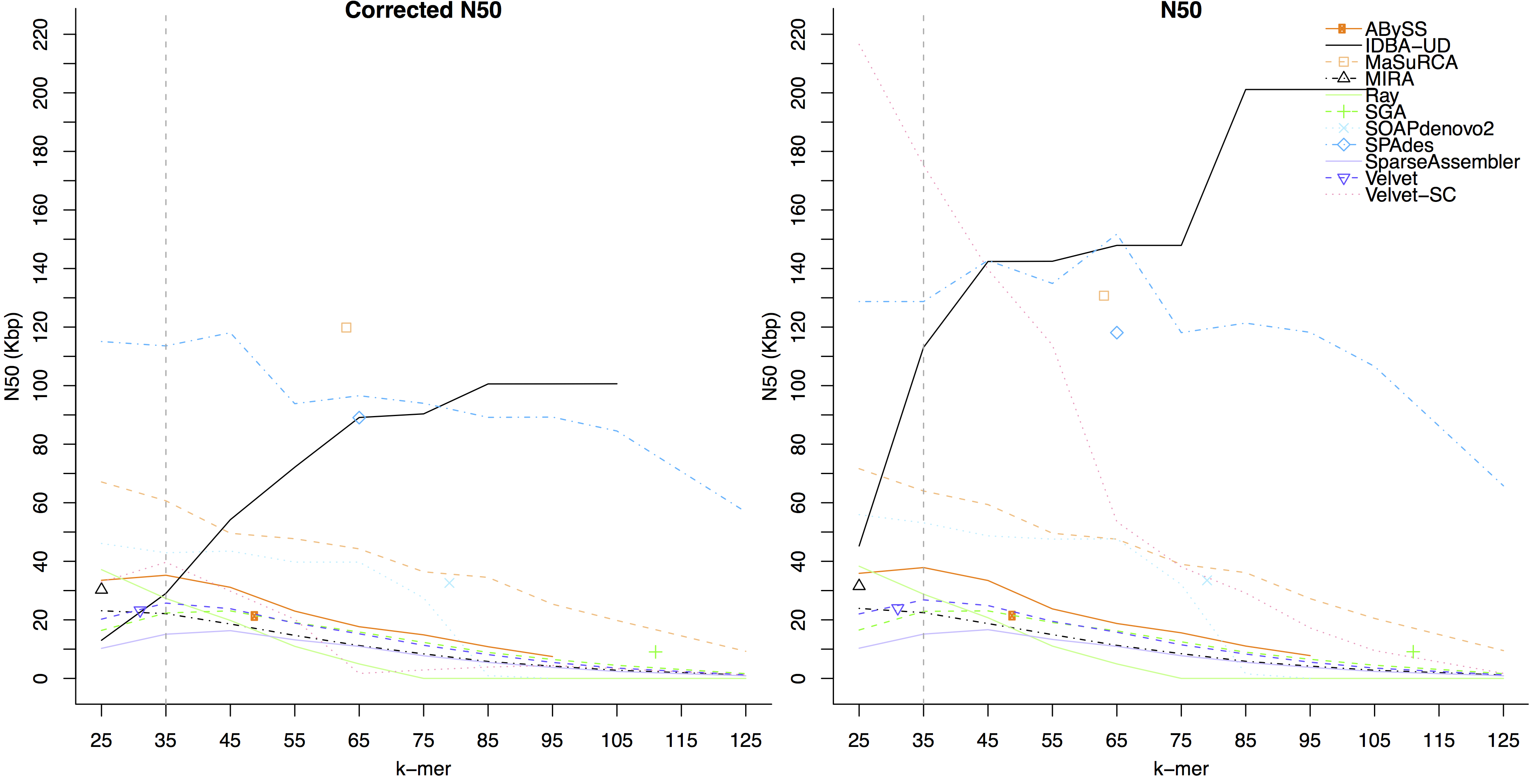
On this dataset, the assemblers which had a higher corrected N50 on trimmed data than untrimmed were:
IDBA-UD, SGA, SparseAssembler, SPAdes, Velvet-SC, and Velvet.
Assembler which had a higher corrected N50 on untrimmed data were:
ABySS, MaSuRCA, MIRA, Ray, and SOAPdenovo2.
- Q:
- What taxonomic classification method should I be using?
- A:
- Good question! But in our experience there is no single method to universally recommend. If you’d like a ultrafast method with great precision but are less worried about sensitivity, Kraken performs well. If you are less concerned about assigning labels to contigs/reads and would rather like to phylogenetically place your reads/contigs w.r.t marker genes, PhyloSift is recommended.
- Q:
- Help! The frozen binary will not extract or unexpectedly crashes.
- A:
The most common reason for this occuring is a lack of free space in the /tmp directory. So first double check that the temporary directory has sufficient space and permissions for the current user. By default, PyInstaller will search a standard list of directories and sets tempdir to the first one which the calling user can create files in. On most systems this will be:
$/tmp/_MEI*
- The list is:
- The directory named by the TMPDIR environment variable.
- The directory named by the TEMP environment variable.
- The directory named by the TMP environment variable.
If your system is missing all of the above, or all of the directories have insufficient free space, runPipeline will not be able to extract itself and will fail while running (see github issue #121 )